Russian original paper
Long Wave Computational Experiments in the Sea Phenomena Studies and other Ocean Fluidmechanics Simulation
V.N. Khramushin, V.A. Shustin, T.N. Ivelskaya *) A.A. Poplavsky **)
Computational Fluid Mechanics and Oceanography lab of SRB
*) Sakhalin Tsunami Warning Center
**) Tsunami lab. of IMG&G
The work is being done with support of Russian Foundation of Basic Researches, grant № 97.05.66037
In this work the materials of researches are shown in the area of computational simulation of the ocean long-wave dynamics, by results of which there are complex computing experiments intended for study of various hydrodynamic processes in ocean and its coastal zone. The researches are primary directed toward making of highly effective methods of tsunami forecast, storm surges and other dangerous sea phenomena. Wide of soluble tasks now is extended by simulation of tidal and current both dynamic interaction of an atmosphere and ocean surface, that has allowed not only to study in details features of computing models, but also to get new knowledge of nature of hydrodynamic processes in ocean.
The goal of researches is the systematic studing of computational experiments in oceanography fluid mechanics, searching of base quality criteria for the fluid dynamics simulation, development of techniques and special computer software for using in duty services of supervision behind a condition of the sea. The decision of many tasks of long-wave dynamics of ocean can be quite removed on a level of daily toolkit as CAD of the duty oceanography-engineer. The potential customers of software is the Tsunami Centre and Sea departments the Sakhalin Weather Services, therefore filling of computer complexes by mathematical models, by interfaces of management and preparation of the initial data is to the greatest degree caused by features of work of these services.
In present complex of oceanologic computational experiments the solution of the following problems is realized:
The listed methods and variants of use of a special software were developed with the purpose of their subsequent introduction in services of the operative warning about danger of sea floods and tsunami of Sakhalin Weather Services. It explains main features of a software - flexibility at definition of setting part of computing experiments and high speed of calculations.
In realization of program complexes the opportunity of fast replacement or additions of other models of hydrodynamics both conditions of an atmosphere interaction and ocean is stipulated, that allows to hope for cooperation to other scientists - oceanologists, interested both in use of computing experiments, and in practical realization mathematical and oceanologic models. With this purpose all program complexes and the saved bases of oceanology data can be submitted for study and free use, including together programs with all initial texts and documentation about their use.
On the basis of our (available as freeware) software the performance the fast express train - analysis of hydrodynamical processes at ocean and near to coast, also realization of complete numerical simulation of tidal a mode, influence on a surface of the sea is possible on the part of atmospheric cyclones and seismic tsunami.
Simulation of storm surges is based well for qualitative testing of computing experiments in long-wave fluidmechanics, for which external revolting influence usually is known on the part of an atmosphere, which can be compared with tide gage records. The similar calculations for tidal mode should take into account dynamics of all world ocean, that requires too large computing resources. The least complexities arise about simulation of a tsunami, but for this dangerous sea phenomenon the mechanism of generation of waves in a source is not usually known.
Real the simulation of interaction of an atmosphere and ocean demands the sanction of set of the unexplored questions connected to transformation of a wind power in long-wave phenomena or coastal currents (lerhs). Such redistribution of energy essentially depends on time of action of storm excitement, extensiveness of a shallow shelf. However, for initial stages of development of storm floods the main role is played by "ship" waves produced by a cyclone in a shallow shelf zone.
Huge researches is necessary for study of transformation features of long-wave phenomena on shallow sites of distribution routes of long waves between open water areas and site tide-gauges, the computing experiments should be compared to results of which measurements. It is necessary for adaptation numerical simulation results of limited computing resources, when the correctness of accounts is provided only in deep-water sites of water areas, without an opportunity of distribution of results of simulation direct to shore line at coast.
Results of expert assessment for a kinematic long-wave simulation
For a rapid analysis of hydrodynamical processes at ocean it is convenient to use simplified kinematic model of distribution of long waves, which allows to make isochronous cards and beams (isolines of wave fronts of directions of their movement). At simulation of long-wave processes these procedures can be used for the express train - analysis of kinematics of wave processes, for example: with the purpose of approached axtrapolation of the data of sea condition incoming from look-out stations.
Kinematics model of long waves distribution allow to make mapping of routes of distribution of wave energy, both for local sources, and in case of the approach of waves from other water areas of the Pasific or the sea of Okhotsk. The Yuzhno-Kuril strait is boundary water area of the sea of Okhotsk, the complexity of a relief which ground does not allow to formalize precomputations as generalized nomograms, but, taking into account, that on modern computers kinematic calculations are carried out very quickly, operative use appropriate of kinematic models can supply the deeper expert analysis and forecast of dangerous sea floods.

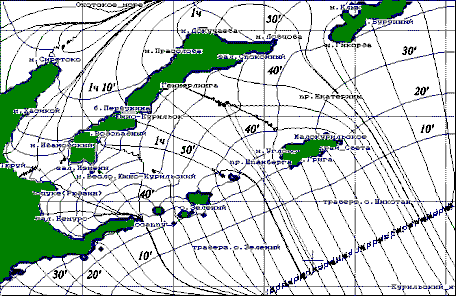
Figure 1. The orthogonal grid of long-wave fronts and beams constructed by a rather direct line extended lengthways of Kuril - Kamchatka trough. Figure shows a direction and change of intensity of long-wave responses near to southern Kuril islands on hydrodynamical processes in the Pasific. The isochronous grid is constructed with an interval 10 minutes, the beams show characteristic concentration/decrease of wave energy near to coast.
The most evident representation of results of such simulation is made out as cards with a isochronous grid (Figure 1), fixing wave fronts through equal intervals of time, is perpendicular to which the lines of beams - directions of distribution of wave energy are under construction. There where on such curvilinear grid the convergence of beams and return curvature of wave fronts is observed, - in this area it is necessary to expect essential strengthening of the first introduction of waves storm surges and tsunami. In regions, where isochrones become frequent (pass much closer one from another), it is necessary to expect strengthening of own fluctuations, which period can be estimated by summation of intervals between quickened isochrones.
From figure above follows, that Yuzhno-Kurilsk city is located between two central lines (Figure 1), concentrating wave energy of front of the first introduction of a tsunami in the south, - in area of cape Vodopadny and in north, - in area of cape of Gimmerling. It means, that in a case of Pacific tsunami ("atmospheric tsunami" - including) Yuzhno-Kurilsk can have harbingers as waves of not so high amplitude, that, unfortunately, the yet absence of large floods does not guarantee at the approach of the subsequent waves, which accumulate in themselves energy in a range of own frequencies of water area of Yuzhno-Kuril strait.
For an estimation of own fluctuations at coast of the sea of Okhotsk the account of the response all of the sea of Okhotsk and of pacific shelf of Kuril islands on the individual wave pulse which has come on the part of the Pasific ocean is executed long in time. As it usually happens, the entering pulse with a period 1 hour was not displayed in any way in spectra of own fluctuations.
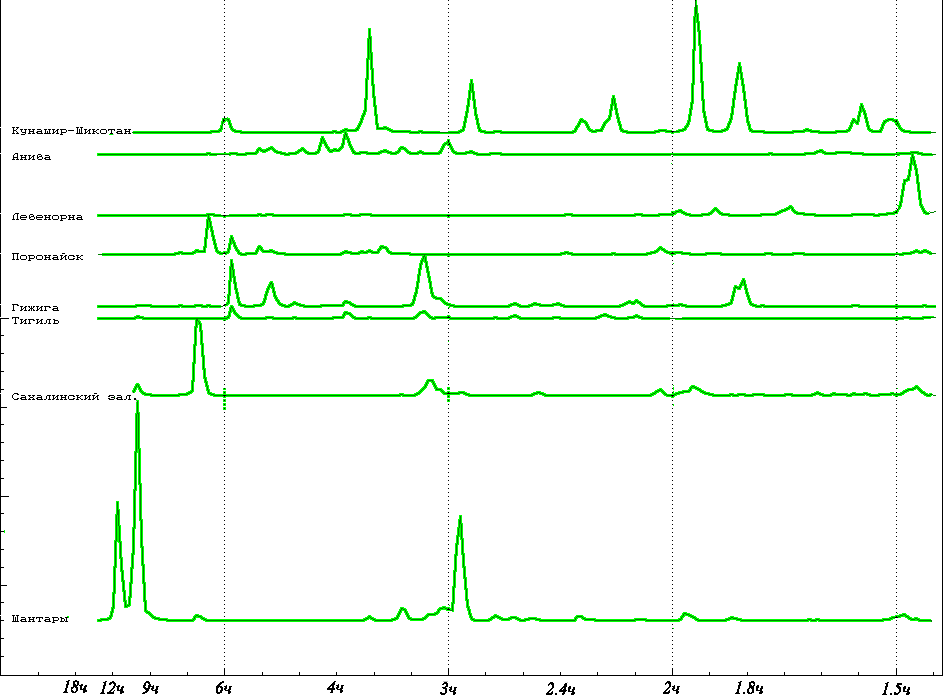
Figure 2. Spectral estimations of periods of own fluctuations inherent in various coastal water areas of the sea of Okhotsk and Kurily Islands
In figure above is shown, that the hydrodynamical shelf activity of Southern Kuril islands is displayed as a chord of own periods of long-wave fluctuations in 2, 3 and 4 hours, thus the intensity of fluctuations is comparable on energy to area of Shantar islands. Good quality of Yuzhno-Kuril strait as long-wave oscillator explains often displays of sea floods. For the same reason in Yuzhno-Kuril strait occur long in time of fluctuation of a sea level initiated by short and individual pulses of a tsunami.
The fact of tidal abnormality before earthquake 5.10.94 г
Two cyclones previous to earthquake of October 4, 1994. From the preliminary analysis of tide-gauge records of a tsunami it is well visible, that the tsunami has taken place on a background essentially tidal mode abnormality.
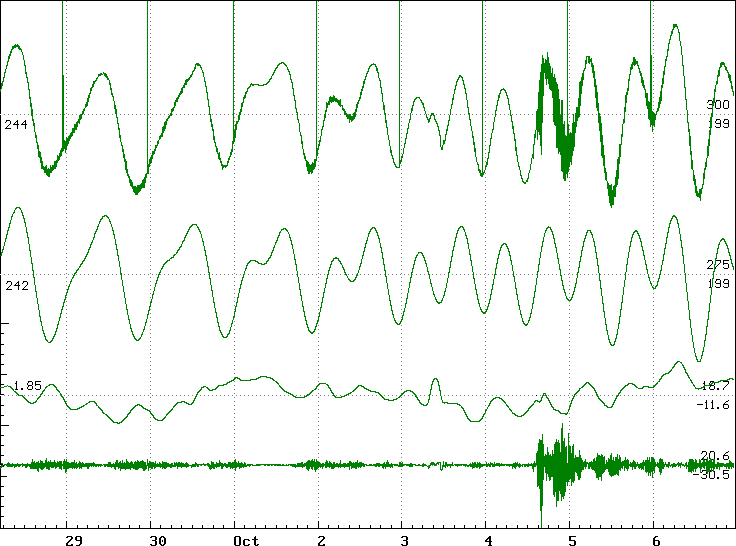
Figure 3. From above downwards are shown: 1 - observеd; 2 - precomputational tide-gauge records, 3-I the record shows a course of storm surge (of put out tide), on fourth - the high-frequency component of storm surge and tsunami of October 4-5, 1994 is given
Are shown tide-gauge records in Kurilsk (Figure 3), item at coast of the sea of Okhotsk. On мореограмме is well seen storm surge, on which background of October 3-4 the fluctuations of the sea with periods close to tidal were displayed. It is possible, that the additional fluctuations of a sea level are caused " nonlinear " by interaction of tide and storm surge, which, together with earth's floods has resulted to overstrain of earth's crust, that was by a push for the strongest earthquake of October 4, 1994.
The direct computing experiments are intended for direct and complete simulation of hydrodynamical processes. They require rather large computing resources and allow to receive results after realization long in time of accounts. Nevertheless, it is always possible to pick up initial given so that the simulated processes proceeded faster than real sea phenomena, providing the decision of prognostic tasks. In practice such simulation can be carried out in a background mode, continuously showing development of the dangerous sea phenomena on the screen of the COMPUTER. Accordingly, in process of receipt of the specified supervision, given from posts simulated processes owe or adapt for the specified initial data, or to renew simulation with use of new conditions.
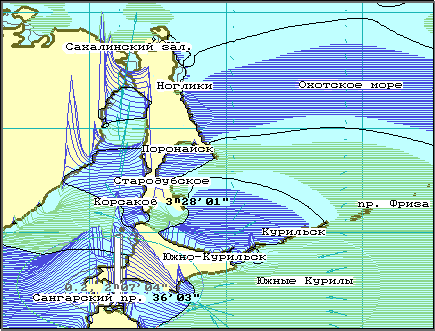
Figure 4. Characteristic change of a sea level and display of seiche fluctuations near to coast under influence of a cyclone, past above Southern Kurils on September 30, 5 days prior to earthquake and tsunami of October 4, 1997. The size of extreme sea levels in settlement area does not exceed yet 30 см, observable Seaside coast of a Tatarsky strait
By results of numerical simulation of a cyclone of September 30 1994 (Figure 4) is possible to make an estimation of long-wave reverberation in various coastal areas. Thus it is marked, that atmospheric cyclones it is necessary raise own fluctuations just in shallow coastal water areas, which intensity strongly is displayed on frequencies of the own fluctuations, present in appreciated earlier chords.
By results of computing experiments water area Southern Kurils should be referred to areas of the greatest repeatability of the dangerous sea phenomena. But, the increased concentration of long-wave energy on the limited water area should have by a consequence the increased variability of loading on ground, that in turn (probably it is just so) can result in the increased seismic activity of all region. The given assumption can be checked up with the help of the information which has been built - in in computing experiments as the computer catalogues of events of a tsunami and as archives of digital tide-gauge records of flood, storm surges and tsunami.
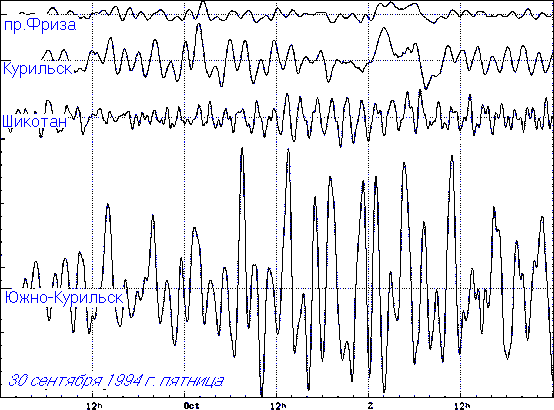
Figure 5. Displays of a cyclone of September 30, 1994 in a strait Frieze, close to Kurilsk, island Shikotan and on a shelf close to Yuzhno-Kurilsk. On the left border of figure the scale of amplitudes with marks through 5 cm is shown
It is necessary to note that the direct affinity deep-water Kuril depression provides fast distribution of long-wave energy on all water area of the sea of Okhotsk, as was marked additional by long-wave fluctuations on tidal-gauges in settlements of Kurilsk and Starodubsk.
Figure 5 once again illustrates essential strengthening of long-wave processes on Yuzhno-Kuril shelf
Statement of problem for tidal simulation on the sea of Okhotsk
The more difficult block of computational experiments realized in a working software, is intended for simulation of tidal mode of sea level and mode of tidal currents in complete flows.
| A) The first hour of simulated tidal process | B) For the tenth day tidal mode approach to real |
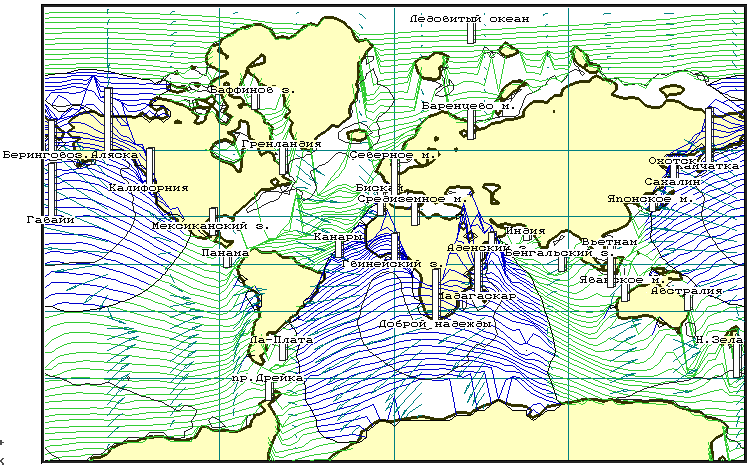
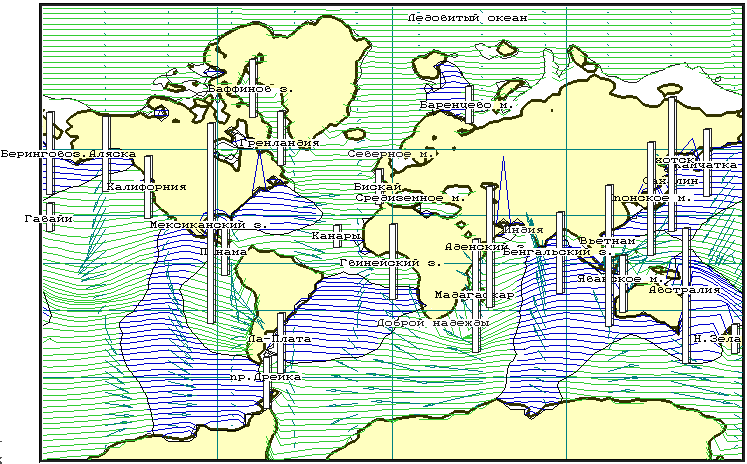
Figure 6 Images on the graphic screen of the COMPUTER during realization of computing experiment on direct simulation of tidal a mode for all Globe. The tide is caused by influence of gravitational fields of the Moon and Sun. Proceeding from spatial approximating criteria caused by limited computing resources, from accounts the large part of a continental shelf is excluded
For testing of tidal models it is necessary to realize direct computing experiments on water area of all World ocean, that, in view of the limited computing resources, allows to make only qualitative estimation of a correctness of physical statement of a task.
The sea of Okhotsk is unique region for research of tidal mode and mode of currents in the partially closed water areas, as for it the division of tide creating forces on external is possible, tidal waves which have come from the Pasific, and internal - formed under influence of astronomical forces is direct on a surface of the sea of Okhotsk. The important factor for a choice of the sea of Okhotsk is that tidal mode is studied many items of coast, that allows to realize qualitative check of numerical models, boundary conditions and methods of generation of wave fluctuations of a level and currents.
If in one of computers makes continuous simulation of tidal mode for the sea of Okhotsk as a whole, then, in case of getting the data about an atmospheric cyclone or earthquake that causes tsunami, on the other computer it is possible to duplicate simulation and to add to account additional conditions for an estimation of danger of storm surges or tsunami waves.
In the given below experiment the simulation is executed which has duration in real time about 1 year.
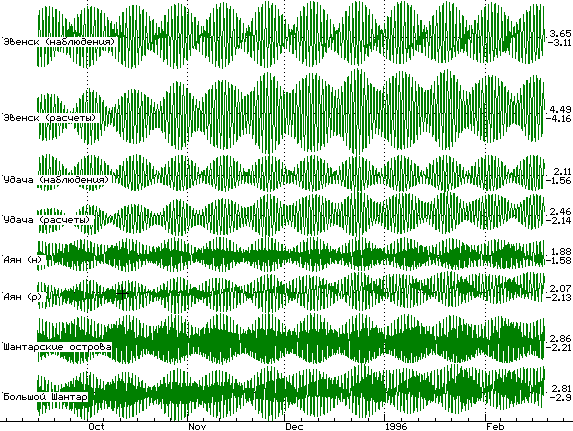
Figure 7. Mutual comparison of observed (upper line) and restored (lower line) tide in several items of the Okhotsk Sea removed from generators of compelled fluctuations. The figures on the right show the maximal and minimal value of a sea level. The marks on the left border set a scale scale with a step of 1 meter
With the help of mutual comparison of the tide-gauge records is judged the fact of qualitative restoration of tidal mode in the sea of Okhotsk. In the present version of the program the algorithms for simulation influence of atmospheric cyclones and tsunami are realized also, which numerical simulation can be carried out in common, or with participation previously stabilized of tidal areas.
In the described above computing experiment it was not possible with sufficient accuracy to execute simulation high-frequency making of tidal fluctuations of a sea level, which will be formed under influence of forces of an astronomical nature directly on a surface of the sea of Okhotsk. As from real observations of tidal mode this component of tide cannot be allocated, for testing the appropriate computing model the decision on realization of computing experiments on a surface of all Globe (Figure 6) was accepted.
Writing about use of computing experiments in conditions of working operative services we know the practical importance such simulation will get only after interface of computers carrying out accounts with sources of the digital information acting from Sakhlin Weather Services and Sakhalin Seismic Service. The operative data should be used in numerical simulation for specification or adaptation computing monitoring to real conditions in the sea.
It is possible to carry out similar accounts, certainly, in retrospective review, for example, for specification of results of forwarding researches or for the analysis of drift of impurity and plankton. The direct numerical simulation requires more time for calculation, during which use of current results for the express train of the analysis or preliminary forecast of consequences of the dangerous sea phenomena, for example - with use of empirical models is possible.
Conclusion
To the present moment in laboratory of the Computing hydromechanics and oceanography SRB active researches of hydrodynamical models are conducted on the basis of long waves in complete flows. In case of application of such simulation for the decision of practical tasks of operative monitoring of sea condition, the circle of tasks can be essentially extended, depending on efficiency of getting and quality of the measuring systems and look-out stations.
The realization and introduction of hydrodynamical computing experiments is the most priority task, which can allow in the shortest terms to solve the whole complex of modern tasks of monitoring and control of the dangerous sea phenomena. For use of this toolkit there are enough of initial given working operative services, acting according to the rules, Sakhalin Weather Services and Sakhlin Seismic Service, which subsequently should formulate and to realize the concept of complex monitoring of sea water areas in Sakhalin region.
All complex of software is offered for free use for the scientific purposes, with the purpose of joint testing and perfection of the mathematical models, incorporated it, and also with the purpose of experienced operation in working services of observation the sea condition.
The work is being done with support of Russian Basic Researches Foundation, grant № 97-05-66037